|
Sound tooth
surface: Code 0
There should be no evidence of caries (either no
or questionable change in enamel translucency after prolonged
air drying (approximately 5 seconds)). Surfaces with
developmental defects such as enamel hypoplasias;
fluorosis; tooth wear (attrition,
abrasion and erosion), and extrinsic or
intrinsic stains will be recorded as sound. |
|
|
|
|
First visual change in
enamel: Code 1
When seen wet there is no evidence of any change in
color attributable to carious activity, but after prolonged air drying a
carious opacity is visible that is not consistent with the clinical
appearance of sound enamel
|
|
|
|
|
Distinct visual change in enamel when
viewed wet: Code 2There
is a carious opacity or discoloration that is not consistent with the
clinical appearance of sound enamel (Note: the lesion is still visible
when dry). The lesion is located in close proximity (in touch or within
1 mm) of the gingival margin
|
|
|
|
|
Underlying dark shadow
from dentin with or without localized enamel breakdown: Code 4
This lesion appears as a shadow of discolored dentin
visible through the enamel surface beyond the white or brown spot lesion,
which may or may not show signs of localized breakdown. This appearance
is often seen more easily when the tooth is wet and is a darkening and
intrinsic shadow which may be grey, blue or brown in color.
|
|
 |
|
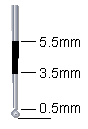
Probe |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Distinct cavity with
visible dentin: Code 5
Cavitation in opaque or discolored enamel exposing the
dentin beneath.
If in doubt, or to confirm the visual assessment, the
CPI probe can be used with NO digital pressure to confirm the presence
of a cavity apparently in dentin. This is achieved by sliding the ball
end along the surface and a dentin cavity is detected if the ball enters
the opening of the cavity and in the opinion of the examiner the base is
in dentin |
|
 |
|
Probe |
|
|
|
 |
|
|
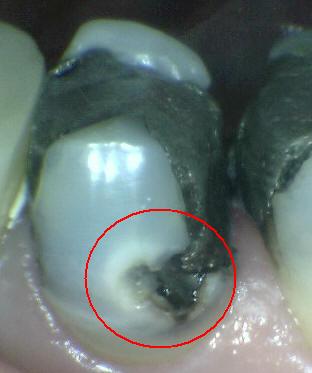
Extensive distinct cavity
with visible dentin: Code 6
Obvious loss of tooth structure, the cavity is both deep
and wide and dentin is clearly visible onv the walls and at the base. An
extensive cavity involves at least half of a tooth surface or possibly
reaching the pulp. |
|
 |
|
Probe |
|
|
|
|
|